Understanding User Personas
User personas are fictional characters created to represent different user types that might use a website, product, or service. They play a crucial role in guiding UX design decisions by providing a clear understanding of users’ needs, behaviors, and preferences.
Why Are User Personas Essential?
- Humanizing Users: Personas humanize data, making it easier for design teams to empathize with and understand users on a personal level.
- Guiding Design Decisions: They act as a compass for design decisions, ensuring that designs cater to the specific goals and needs of the intended user groups.
- Enhancing User-Centricity: Personas shift the focus from assumptions to user-centric design, ensuring that the final product aligns with users’ expectations and desires.
Creating Effective User Personas
- Research-Based Insights: Personas are built on qualitative and quantitative data obtained through user research, interviews, surveys, and analytics.
- Identifying User Goals: They highlight users’ primary goals, motivations, pain points, and behaviors when interacting with the product or service.
- Detail-Oriented Narratives: Personas include demographic information, preferences, behaviors, and scenarios to create a vivid representation of different user types.
Utilizing Personas in Design
- Guiding Design Choices: Personas aid in making informed decisions about features, functionality, layout, and content that resonate with specific user groups.
- Testing and Validation: They serve as a benchmark for testing usability, ensuring that design solutions align with users’ expectations.
- Iterative Improvement: Personas evolve over time as user needs change, enabling designers to continually refine and optimize the user experience.
Importance of User Research in UX Design
User research forms the backbone of successful UX design, providing crucial insights into user behaviors, preferences, and needs. It involves various methodologies aimed at understanding users and their interactions with a product or service.
Gaining Insights Through User Research
- Understanding User Behaviors: Research methods like interviews, observations, and analytics uncover how users interact with a product, highlighting pain points and preferences.
- Identifying User Needs: Research helps in identifying and prioritizing user needs, guiding the creation of solutions that directly address these needs.
- Validating Assumptions: It helps in validating assumptions and reducing design decisions based solely on guesswork or assumptions.
User Research Methods
- User Interviews: Engaging users in open-ended discussions to gather in-depth insights into their motivations, challenges, and preferences.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Collecting quantitative data on user demographics, behaviors, and satisfaction levels.
- Usability Testing: Observing users as they interact with prototypes or existing products to understand usability issues.
Benefits of User Research in UX Design
- Informed Decision Making: User research provides data-backed insights, ensuring design decisions align with user needs and behaviors.
- Enhanced User Satisfaction: By understanding users better, designs can be tailored to meet their expectations, leading to improved satisfaction.
- Cost and Time Savings: Addressing user needs early in the design process reduces the need for costly redesigns later on.
Integrating User Research in the Design Process
- Early and Continuous Research: Conducting research at the outset and throughout the design process ensures a user-centric approach at every stage.
- Collaborative Approach: Involving multidisciplinary teams in research ensures diverse perspectives and holistic insights.
- Iterative Improvement: Using research findings for iterative improvements ensures that designs evolve based on user feedback and changing needs.
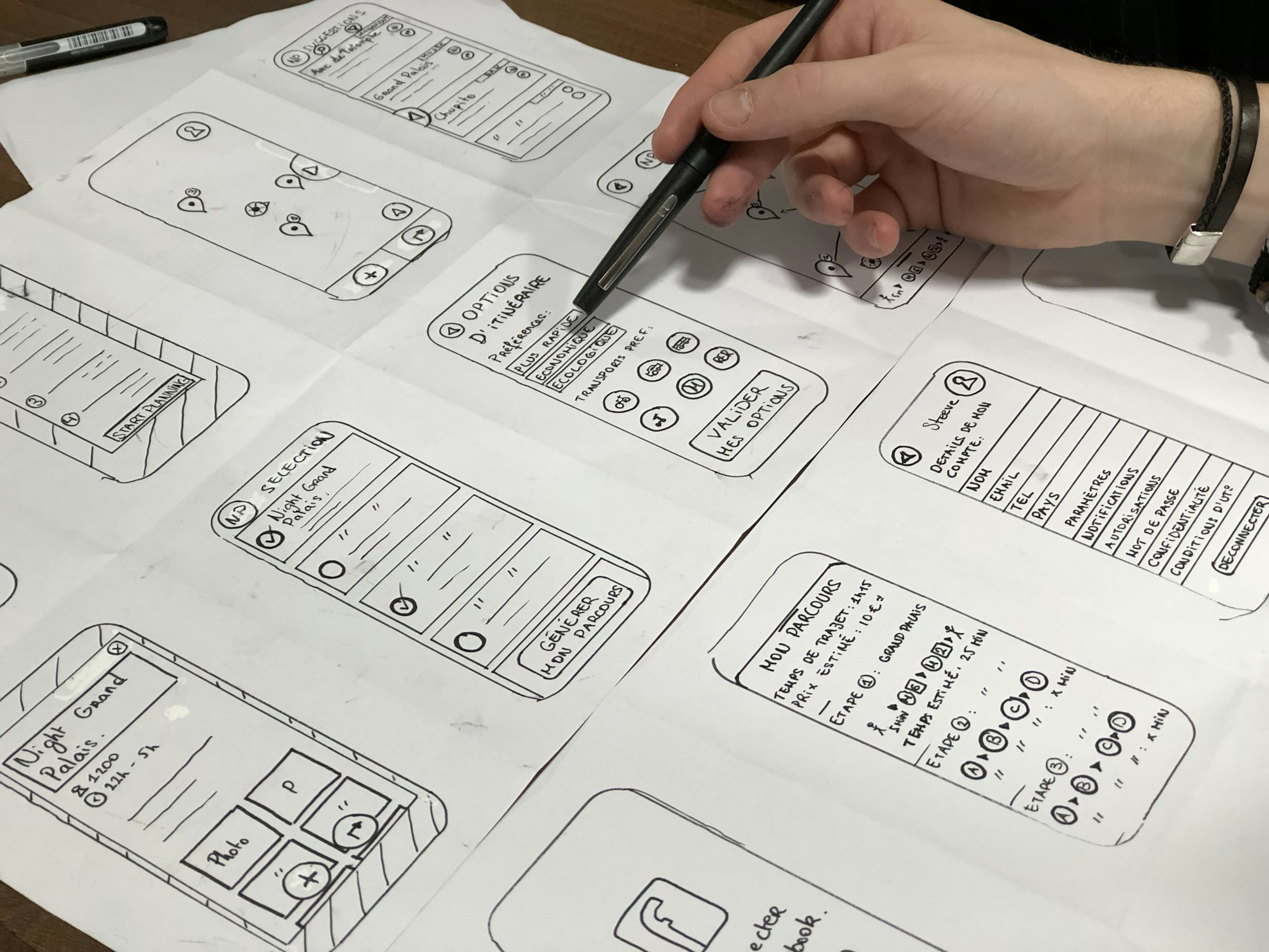
Wireframing and Prototyping
Wireframing and prototyping are essential steps in the UX design process, offering visual representations that help in conceptualizing and refining designs before implementation.
Understanding Wireframes and Prototypes
- Wireframes: Wireframes are basic visual representations that outline the structure and layout of a design, focusing on functionality and content placement without detailed design elements.
- Prototypes: Prototypes are interactive, more detailed versions of designs, allowing users to interact with and test the functionality and usability of the product.
The Role of Wireframes and Prototypes
- Clarifying Design Structure: Wireframes provide a blueprint for layout and structure, outlining the skeletal framework of a design.
- Testing Functionality: Prototypes allow users to interact with the design, enabling testing of features, usability, and user flows.
Benefits of Wireframing and Prototyping
- Iterative Design Refinement: They facilitate iterative improvements, allowing for quick iterations and refinements based on user feedback.
- Early Problem Identification: Identifying usability issues and design flaws early in the process, reducing costly redesigns in later stages.
Wireframing and Prototyping Tools
- Wireframing Tools: Software like Sketch, Adobe XD, or Balsamiq simplifies the creation of wireframes with drag-and-drop functionalities.
- Prototyping Tools: Tools like InVision or Figma facilitate the creation of interactive prototypes, allowing for user testing and feedback.
Integrating Wireframes and Prototypes in UX Design
- Starting Point for Design: They serve as a starting point for design discussions, ensuring alignment between stakeholders and designers.
- Usability Testing: Prototypes aid in usability testing, gathering valuable user insights to refine and enhance the design.
Usability Testing Techniques
Usability testing involves evaluating a product by testing it with representative users to gather insights into its effectiveness, efficiency, and user satisfaction. These techniques aid in identifying usability issues and refining the user experience.
Importance of Usability Testing
- User-Centric Approach: It ensures that design decisions are based on user feedback and align with user expectations and behaviors.
- Identifying Pain Points: Usability testing uncovers issues or challenges users face while interacting with the product, providing opportunities for improvement.
Usability Testing Methods
- Moderated Testing: Conducted in a controlled environment with a moderator guiding users through predefined tasks while observing and collecting feedback.
- Unmoderated Remote Testing: Users complete tasks remotely, providing feedback through screen recordings or questionnaires without direct supervision.
- A/B Testing: Comparing two versions of a design or feature to determine which performs better in achieving specific goals.
- Heuristic Evaluation: Experts evaluate the design based on recognized usability principles or heuristics to identify potential issues.
Selecting Participants for Usability Testing
- Representative Users: Users chosen for testing should represent the target audience or personas of the product.
- Sample Size: While smaller sample sizes can uncover significant issues, larger samples provide more statistically significant data.
Conducting Usability Testing
- Task-Based Approach: Design tasks that users are likely to perform with the product to observe their interactions and gather feedback.
- Collecting and Analyzing Data: Gather feedback through observation, interviews, or surveys and analyze the data to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
Iterative Nature of Usability Testing
- Continuous Improvement: Usability testing is an ongoing process, with multiple iterations to refine and enhance the user experience.
- Feedback Integration: Incorporate user feedback and insights into subsequent design iterations to address identified issues.
Accessibility in UX Design
Accessibility in UX design ensures that digital products and services are usable by people of all abilities and disabilities. It involves designing and developing with considerations for diverse user needs.
Understanding Accessibility in UX Design
- Inclusive Design: It involves designing products that can be used by individuals with disabilities without the need for adaptation or specialized designs.
- Legal and Ethical Obligations: Accessibility is not only a legal requirement in many regions but also an ethical responsibility to ensure equal access to information and services.
Key Aspects of Accessibility
- Perceivable: Design content that can be perceived by all users, including those with visual or auditory impairments, through alternative text, captions, or audio descriptions.
- Operable: Ensure that products are navigable and operable through various input methods, accommodating users with mobility or dexterity impairments.
- Understandable: Create interfaces and content that are easy to understand, accommodating users with cognitive or learning disabilities.
- Robust: Design products that can be interpreted reliably by a wide range of assistive technologies.
Designing for Accessibility
- Semantic HTML: Use semantic HTML to create a clear document structure that aids screen readers and other assistive technologies.
- Color and Contrast: Ensure sufficient color contrast for text and backgrounds to aid users with visual impairments.
- Keyboard Accessibility: Design interfaces that can be navigated using keyboard-only navigation, supporting users who cannot use a mouse.
User Testing for Accessibility
- Involving Diverse Users: Involve users with disabilities in usability testing to identify accessibility issues and gather firsthand feedback.
- Accessibility Audits: Conduct regular accessibility audits to ensure ongoing compliance with accessibility standards and guidelines.
Benefits of Accessibility in UX Design
- Expanded User Base: Designing for accessibility increases the usability of products for everyone, not just users with disabilities.
- Positive Brand Image: Demonstrating a commitment to accessibility can enhance a brand’s reputation and inclusivity.
Visual and Interaction Design Principles
Visual and interaction design principles play a crucial role in creating engaging, intuitive, and aesthetically pleasing user experiences. These principles guide the creation of interfaces that are not only functional but also visually appealing and easy to use.
Understanding Visual Design Principles
- Consistency: Establish consistent design elements such as colors, fonts, and layouts to create a cohesive and predictable user experience.
- Hierarchy: Use visual cues like size, color, and contrast to prioritize information and guide users’ attention to key elements.
- Balance: Distribute visual elements evenly across the interface to create a sense of equilibrium and avoid overwhelming the user.
Key Interaction Design Principles
- Feedback: Provide immediate and clear feedback to users when they interact with elements, ensuring that their actions are acknowledged.
- Affordance: Design elements in a way that suggests their functionality or purpose, making it intuitive for users to interact with them.
- User Control: Allow users to control their interactions, enabling them to navigate and manipulate the interface at their own pace.
Role of Visual and Interaction Design in UX
- Enhancing Usability: Clear visual hierarchy and intuitive interaction elements contribute to a smoother and more intuitive user experience.
- Emotional Engagement: Thoughtful visual design evokes emotions, influencing users’ perceptions and creating memorable experiences.
Applying Design Principles
- Typography and Readability: Use legible fonts and appropriate typography to ensure readability across different devices.
- Visual Consistency: Maintain a consistent design language throughout the interface, ensuring coherence and ease of use.
Designing for Different Devices and Contexts
- Responsive Design: Create designs that adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes and devices, prioritizing mobile responsiveness.
- Contextual Design: Consider the context in which users interact with the product to tailor the design accordingly.
Information Architecture and Navigation Design
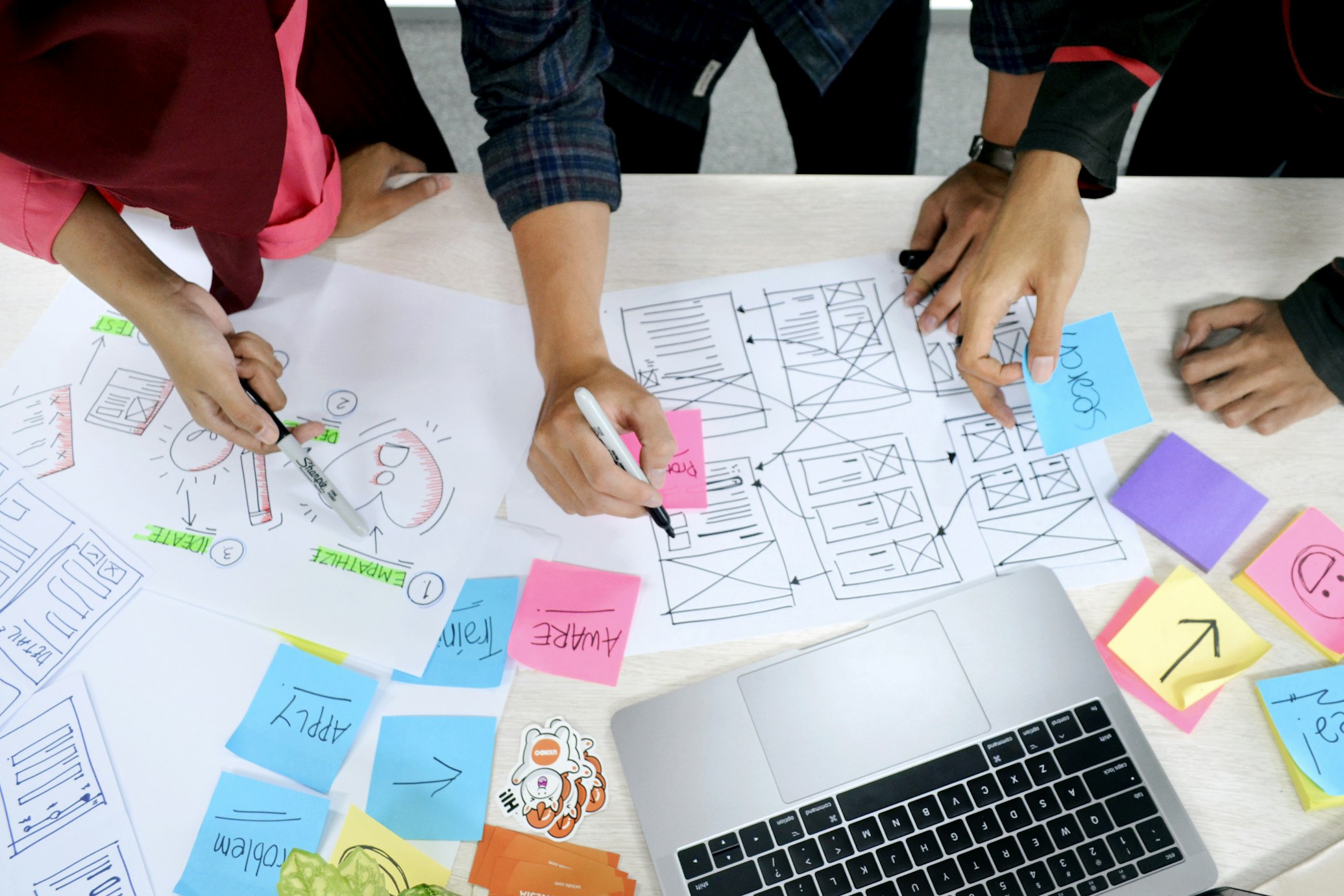

Information architecture (IA) and navigation design are fundamental aspects of UX design, focusing on organizing and structuring content in a way that facilitates intuitive navigation and comprehension for users.
Understanding Information Architecture (IA)
- Content Organization: IA involves organizing and structuring content to make it easily accessible and understandable to users.
- Hierarchical Structure: It establishes a clear hierarchy, grouping related content and ensuring logical relationships between different sections.
Key Aspects of Navigation Design
- Clear Navigation Paths: Design intuitive navigation menus and pathways that guide users to desired information or actions.
- Wayfinding Elements: Implement visual cues and wayfinding elements like breadcrumbs or search bars to aid users in navigating complex interfaces.
Importance of Information Architecture and Navigation
- Enhanced Usability: Well-structured IA and navigation design improve usability, allowing users to find information efficiently.
- Reduced Cognitive Load: Clear navigation reduces the cognitive effort required for users to understand and interact with the interface.
Designing Effective Information Architecture
- User-Centric Approach: Design IA based on user research and understanding of users’ mental models and expectations.
- Card Sorting: Use card sorting techniques to involve users in organizing and categorizing content, ensuring it aligns with their mental models.
Optimizing Navigation Design
- Mobile-Friendly Navigation: Ensure navigation is optimized for mobile devices, considering limited screen space and touch interactions.
- Consistency and Predictability: Maintain consistent navigation patterns and placement across different sections for a predictable user experience.
Testing and Iterating Navigation Design
- Usability Testing: Conduct usability tests to evaluate the effectiveness of navigation and gather user feedback for iterative improvements.
- Analytics and Iteration: Use analytics data to identify navigation issues and iteratively refine the navigation based on user behavior.
Feedback Loops and Iterative Design
Feedback loops and iterative design are integral components of the UX design process, enabling continuous refinement and improvement of products based on user feedback and evolving needs.
Understanding Feedback Loops
- Continuous User Input: Feedback loops involve gathering feedback from users at various stages of the design process to inform improvements.
- Multi-Channel Feedback: Collect feedback through user testing, surveys, analytics, and direct user interactions to gain diverse insights.
Importance of Iterative Design
- Continuous Improvement: Iterative design allows for gradual enhancements based on user feedback, avoiding costly overhauls and ensuring ongoing improvements.
- Adapting to Changing Needs: It accommodates changing user needs and technological advancements by allowing designs to evolve over time.
Feedback Loop Stages in UX Design
- Collection and Analysis: Gather user feedback through various channels and analyze it to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
- Implementation and Testing: Implement design changes based on feedback and test them to evaluate their effectiveness.
Iterative Design Process
- Prototyping and Testing: Create prototypes, test them with users, gather feedback, and iterate on design elements.
- Refinement and Validation: Refine design solutions based on user feedback and validate improvements through further testing.
Benefits of Feedback Loops and Iterative Design
- User-Centered Solutions: Continuous feedback ensures that designs align with user needs and preferences.
- Reduced Risk: Iterative design mitigates the risk of creating products that do not meet user expectations by incorporating user feedback early and frequently.
Implementing Effective Feedback Loops
- Early and Often: Start gathering feedback early in the design process and continue throughout the product’s lifecycle.
- Engaging Stakeholders: Involve stakeholders, designers, developers, and users in feedback loops to gather diverse perspectives.
Measuring Success Through Iteration
- Metrics-Driven Design: Use metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of design iterations.
- A/B Testing: Test different design variations to determine which performs better in achieving specific goals.





